what is stainless steel made of
what is stainless steel
Stainless steel is a corrosion-resistant alloy steel that is mainly composed of iron and contains at least 10.5% chromium. Chromium forms a dense chromium oxide film on the surface of stainless steel, preventing further oxidation and corrosion. In addition to chromium, other elements are often added to stainless steel to improve its properties.
Types of stainless steel are mainly divided into the following categories:
Austenitic stainless steel: The most common type, containing higher nickel and chromium, has good corrosion resistance and plasticity, and is often used in food processing and chemical equipment.
Ferritic stainless steel: It contains higher chromium but lower nickel content, is magnetic, and is often used in automobile exhaust pipes and household appliances.
Martensitic stainless steel: high hardness, good wear resistance, commonly used in knives and bearings.
Duplex stainless steel: has the characteristics of both austenite and ferrite, high strength and corrosion resistance, suitable for marine engineering and chemical industry.
what stainless steel is made of
Nickel: Improves corrosion resistance and toughness, common in austenitic stainless steel.
Molybdenum: Enhances resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, common in stainless steel for marine environments.
Titanium: Prevents intergranular corrosion and stabilizes carbides.
Nitrogen: Improves strength and corrosion resistance, common in duplex stainless steel.
Manganese: Improves strength and processing properties.
Copper: Improves acid resistance and processing properties.
how stainless steel is produced?
Walmay Metal, a stainless steel manufacturing, takes the production of stainless steel sheets as an example and describes in detail the various steps and their reasons:
1. Melting
Process: Iron, chromium, nickel and other raw materials are melted into molten steel at high temperature in an electric arc furnace or induction furnace, usually at a temperature of about 1600°C.
Reason: Converting solid raw materials into liquid form facilitates subsequent composition adjustment and impurity removal.
2. Removing Carbon Content
One-step method (batch melting method): various raw materials, such as nickel plate, pure iron, scrap stainless steel, ferrochrome, etc., are placed in an electric furnace and energized to melt and produce stainless steel.
This method is used in specific cases (such as the production of 400 series stainless steel).
Two-step method (double steelmaking method): Roughing equipment (arc furnace or converter) is combined with refining equipment (AOD furnace or VOD furnace). The molten steel melted by nickel-containing pig iron, high-carbon ferrochrome and scrap steel in an electric arc furnace is added to AOD/VOD for decarburization.
This method is widely used in the production of most stainless steel varieties.
Three-step method (triple steelmaking method): EAF→AOD→VOD smelting process combines the advantages of AOD and VOD.
It is used to produce high-end varieties such as ultra-low carbon, nitrogen-controlled or nitrogen-containing stainless steel and ultra-pure ferritic stainless steel.

3. Tuning
Process: Adjust the content of elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum according to the type of stainless steel.
Reason: Ensure that the stainless steel has the required chemical composition and properties.
4. Forming or Casting
Process: The alloyed molten metal needs to be poured into a mold for casting to obtain the most basic stainless steel casting.
Reason: To convert liquid steel into solid billets for subsequent processing.
5. Hot Rolling
Process: The steel billet is heated to a high temperature (about 1200°C) and formed into a plate by a hot rolling machine. The stainless steel casting is heat treated to adjust its internal composition structure and properties such as hardness and strength.
Reason: Through high-temperature rolling, the thickness is reduced, the length and width are increased, and the stainless steel plate is initially formed to ensure the performance of the stainless steel product.
6. Cold Rolling
Process: The hot-rolled steel plate is further rolled to the target thickness at room temperature. Cold-rolled stainless steel has high dimensional accuracy, low surface roughness, good surface quality and high strength.
Stainless steel cold-rolled steel plate is a stainless steel plate produced by cold rolling process. The thickness is not more than 3mm for thin plate, and the thickness is more than 3mm for thick plate.
Reason: Cold rolling can improve the strength, hardness and surface finish of the plate.
7. Annealing
Process: Heat the cold-rolled plate to an appropriate temperature and then slowly cool it.
For 304L low-carbon stainless steel, annealing is generally carried out between 1080℃-1120℃.
For 304 stainless steel pipes, the annealing temperature is generally around 800℃-900℃.
Reason: To reduce the hardness of the material, improve the plasticity, make it suitable for cutting and cold deformation processing; eliminate internal stress, improve mechanical properties and processing performance; by refining the grains, uniform steel structure and composition, improve the performance of the steel or prepare for subsequent heat treatment.
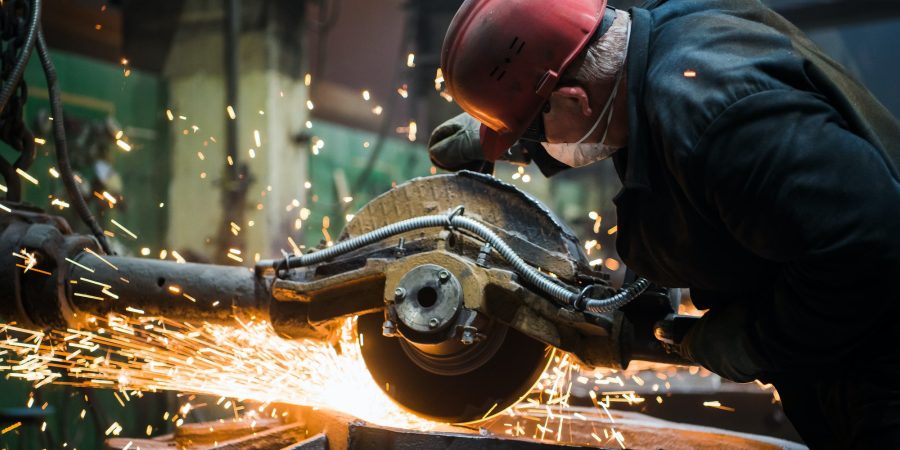

8. Descaling or Pickling
Process: Use acid (such as a mixture of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid) to remove surface oxide scale.
Reason: Remove the surface oxide layer to improve surface quality and corrosion resistance.
9. Processing
Process: Use acid (such as a mixture of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid) to remove surface oxide scale.
Reason: Remove the surface oxide layer to improve surface quality and corrosion resistance.
10. Finishing
Process: Polishing, plating, sandblasting and other surface treatments are performed. The surface of stainless steel products is electroplated, sprayed and other treatments are performed to improve the corrosion resistance and aesthetics of stainless steel materials.
Reason: Improve surface finish and corrosion resistance, meet aesthetic and functional requirements, and enhance the service life and appearance quality of stainless steel products.
Application of stainless steel
Due to its excellent performance, stainless steel is widely used in the following fields:
Architecture and decoration: such as curtain walls, handrails, elevator interiors.
Food and medical: such as kitchen equipment, surgical instruments.
Transportation: such as automobile exhaust pipes, train carriages.
Energy and chemical industry: such as oil pipelines, nuclear power plant equipment.
Summary
In summary, the production of stainless steel is a complex and delicate process involving multiple links such as smelting, casting, heat treatment, processing and surface treatment. Each step requires precise control and professional technology to ensure the quality and performance of the final product.
From raw materials to finished products, stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties to meet a variety of industrial needs.
Stainless steel alloys is widely used in construction, food processing, medical equipment, chemical equipment, automobile manufacturing and other fields, and is an indispensable material in modern industry.
Tags: stainless steel, steel,stainless steel alloys
Recent articles:
- U.S. Stainless Steel Tariffs Jump to 50% – How Companies Are Adapting
- Global Steel Output Drops 5.8% in June – India Bucks the Trend
- Alleima’s New Super Duplex Steel Fights Urea Plant Corrosion
- 310S vs 304 Stainless Steel Pipes: Which Should You Choose?
- 2205 vs 2507 Duplex Stainless Steel: Choosing Your Industrial Champion
- 430 Stainless Steel: The Cost-Effective Workhorse You Should Know About
Table of Contents
Recent Posts
Have Any Question?
High-quality manufacturers in the stainless steel industry, feel free to ask